Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Idomura, Yasuhiro
Physics of Plasmas, 26(12), p.120703_1 - 120703_5, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.23(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This Letter presents the impacts of the hydrogen isotope mass and the normalized gyroradius 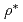 on L-mode like hydrogen (H) and deuterium (D) plasmas dominated by ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. In ion heated numerical experiments with adiabatic electrons, the energy confinement time shows almost no isotope mass dependency, and is determined by Bohm like
on L-mode like hydrogen (H) and deuterium (D) plasmas dominated by ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. In ion heated numerical experiments with adiabatic electrons, the energy confinement time shows almost no isotope mass dependency, and is determined by Bohm like 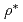 scaling. Electron heated numerical experiments with kinetic electrons show clear isotope mass dependency caused by the isotope effect on the collisional energy transfer from electrons to ions, and the H and D plasmas show similar ion and electron temperature profiles at an H to D heating power ratio of
scaling. Electron heated numerical experiments with kinetic electrons show clear isotope mass dependency caused by the isotope effect on the collisional energy transfer from electrons to ions, and the H and D plasmas show similar ion and electron temperature profiles at an H to D heating power ratio of 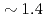 . The normalized collisionless ion gyrokinetic equations for H and D plasmas become identical at the same
. The normalized collisionless ion gyrokinetic equations for H and D plasmas become identical at the same 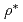 , and collisions weakly affect ITG turbulence. Therefore, the isotope mass dependency is mainly contributed by the
, and collisions weakly affect ITG turbulence. Therefore, the isotope mass dependency is mainly contributed by the 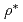 scaling and the heating sources.
scaling and the heating sources.
Suzuya, Kentaro; Kameda, Yasuo*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Yoshida, Koji*; Ito, Keiji*; Fukunaga, Toshiharu*; Misawa, Masakatsu*
Journal of Neutron Research, 13(1-3), p.123 - 128, 2005/03
The design, performance, philosophy, lessons learned and advantages of the neutron total scattering spectrometer for hydrogenous materials, FAST, under consideration for the J-PARC-JSNS, are described. In particular, novel instrumentation concept such as the small fractional scattered neutron flight path,  = L
= L /(L
/(L +L
+L ), where L
), where L is the incident flight path, moderator to sample, L
is the incident flight path, moderator to sample, L is the scattered neutron flight path from sample to detector, is presented and their expected performance at the JSNS is considered.
is the scattered neutron flight path from sample to detector, is presented and their expected performance at the JSNS is considered.
Yamakawa, Koji*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 370(1-2), p.211 - 216, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.41(Chemistry, Physical)The migration of hydrogen in Pd-1at.% Fe-H and Pd-1at.% Ag-H alloys is investigated by electrical resistivity measurement around 50 K. The disordered hydrogen atoms are introduced by electron irradiation with 0.5 MeV electrons below 15 K. The disordered atoms order by migration of hydrogen atoms during the heating-up of the specimens. The recovery curves of electrical resistivity have two sub-stages for electron irradiated specimens and one stage for fast cooled specimens. The migration energy of hydrogen is obtained from the kinetic analysis of the resistivity change due to the ordering, using the cross-cut method for the electron irradiated specimen and fast cooled specimen. The obtained value of the migration energy for the low temperature stage is smaller than that for the high temperature stage. The value for the high temperature stage is similar to the energy for the case of fast cooling. The difference between the hydrogen atoms disordered by irradiation and that by fast cooling is discussed for Pd based alloys.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Kakuta, Toshiya*; Suzuki, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 297(3), p.285 - 291, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:74.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The isotope effect on the implantation-driven permeation of pure tritium (T) and deuterium (D) through nickel was investigated, respectively. The rate-determining processes of backward flow at the upstream surface and permeation at the down-stream surface were found to be as follows: recombination on up-stream surface and diffusion at down-stream side in a lower temperature region, whereas recombination on both surfaces in a higher temperature region for T and D, respectively. The diffusion coefficients of T and D derived by analyzing the obtained transient data of permeation in the lower temperature region were in good agreement with literature data of deuterium. The obtained activation energy of diffusion for T and D suggested the tendency of mass dependence. The surface recombination coefficients for both isotopes were also derived and showed in good agreement with literature data. As a result, the experimental results indicated the surface recombination could be attributed to the isotope effect of the permeation between T and D rather than the diffusion.
 ions with H atoms
ions with H atoms*; Shirai, Toshizo; Shimakura, N.*
Phys. Scr., T73, p.110 - 111, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:19.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 C and Pu sample worths in FCA assembly XVII-1
C and Pu sample worths in FCA assembly XVII-1Nagaya, Yasunobu; Ono, Akio; Osugi, Toshitaka
JAERI-Research 95-003, 40 Pages, 1995/01
no abstracts in English
Hoshiya, Taiji; *; Katsuta, Hiroji; Ando, Hiroei
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 56(7), p.747 - 756, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
Noguchi, Hiroshi; Murata, Mikio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 33(4), p.360 - 362, 1991/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:51.2(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
J.Phys.,C, 19, p.1665 - 1677, 1986/00
no abstracts in English
;
Bunseki Kagaku, 34(11), p.677 - 681, 1985/00
no abstracts in English
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 136, p.1 - 5, 1985/00
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:94.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
*;
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 49(7), p.491 - 494, 1985/00
no abstracts in English
Saeki, Masakatsu; Tachikawa, Enzo; *; *; *
J.Phys.Chem., 88(14), p.3108 - 3110, 1984/00
no abstracts in English
; Araki, Masanori; ; ; ; ; ; Matsuda, Shinzaburo; ; *; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 53(12), p.1864 - 1869, 1982/00
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:87.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Katsuta, Hiroji; Furukawa, Kazuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 18(2), p.143 - 151, 1981/00
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:96.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ikezoe, Yasumasa;
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 48(11), p.3111 - 3113, 1975/11
Times Cited Count:6no abstracts in English
 -irradiation of A-, X-, Y- and mordenite type zeolites in aqueous solution
-irradiation of A-, X-, Y- and mordenite type zeolites in aqueous solutionKumagai, Yuta; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
Zeolite minerals are suitable adsorbents for removal of radioactive cesium in water, because of their high radiation resistances. However, irradiation of zeolites results in decomposition of water adsorbed on the zeolites. Water decomposition produces hydrogen (H ) and hydrogen peroxide (H
) and hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ). H
). H production has a risk of making an explosive gas mixture. H
production has a risk of making an explosive gas mixture. H O
O causes corrosion of metals and alloys. Therefore, the radiation effects are required to be assessed and controlled. In this study, H
causes corrosion of metals and alloys. Therefore, the radiation effects are required to be assessed and controlled. In this study, H and H
and H O
O production by irradiation of zeolites in aqueous solution are comparatively studied among different types of zeolites, A-, X-, Y- and mordenite-types. The mixtures of the zeolites and aqueous solution were irradiated by
production by irradiation of zeolites in aqueous solution are comparatively studied among different types of zeolites, A-, X-, Y- and mordenite-types. The mixtures of the zeolites and aqueous solution were irradiated by  Co
Co  -rays. The A-type and the X-type zeolites produced more H
-rays. The A-type and the X-type zeolites produced more H than the Y-type and the mordenite-type. In contrast, the H
than the Y-type and the mordenite-type. In contrast, the H O
O production was inhibited by the addition of zeolites. The A-type and the X-type zeolites showed remarkable inhibition. The A-type and the X-type contains more aluminum in their frameworks than the others do. Therefore, the results suggest that aluminum sites have an important role in the reactions induced by irradiation.
production was inhibited by the addition of zeolites. The A-type and the X-type zeolites showed remarkable inhibition. The A-type and the X-type contains more aluminum in their frameworks than the others do. Therefore, the results suggest that aluminum sites have an important role in the reactions induced by irradiation.
Thwe Thwe, A.; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Furukawahara, Ryo; Ito, Tatsuya
no journal, ,
For hydrogen safety in the storage of wet radioactive materials under the decommissioning process of nuclear power stations including 1F, not only the experimental but also analytical studies on hydrogen generation from water radiolysis are important. Until now, we have conducted those closely related to the 1F decommissioning by the experiments for the effects of seawater salts, liquid depth and temperature, and by the calculations for the effect of liquid flow. In this study, we calculated the liquid-depth effect on hydrogen generation by using a one-dimensional reaction model in the vertical direction based on the open-source software CANTERA. The division of reaction cells was found to be important. As the division number increased, the slope of the increase in the amount of hydrogen generated with respect to the absorbed dose became smaller, approaching to the experimental results. However, when the number exceeded 100, the calculation results were underestimated under the current experimental and calculation conditions.